Класс Месторождения: Крупное
Тип Месторождения: Нефтегазовое
Местоположение:
Местность:
Стадия разработки: Добыча
Год открытия: 1975
Источник информации:
Метод открытия:
Площадь: 81.09 км²
Hengam field
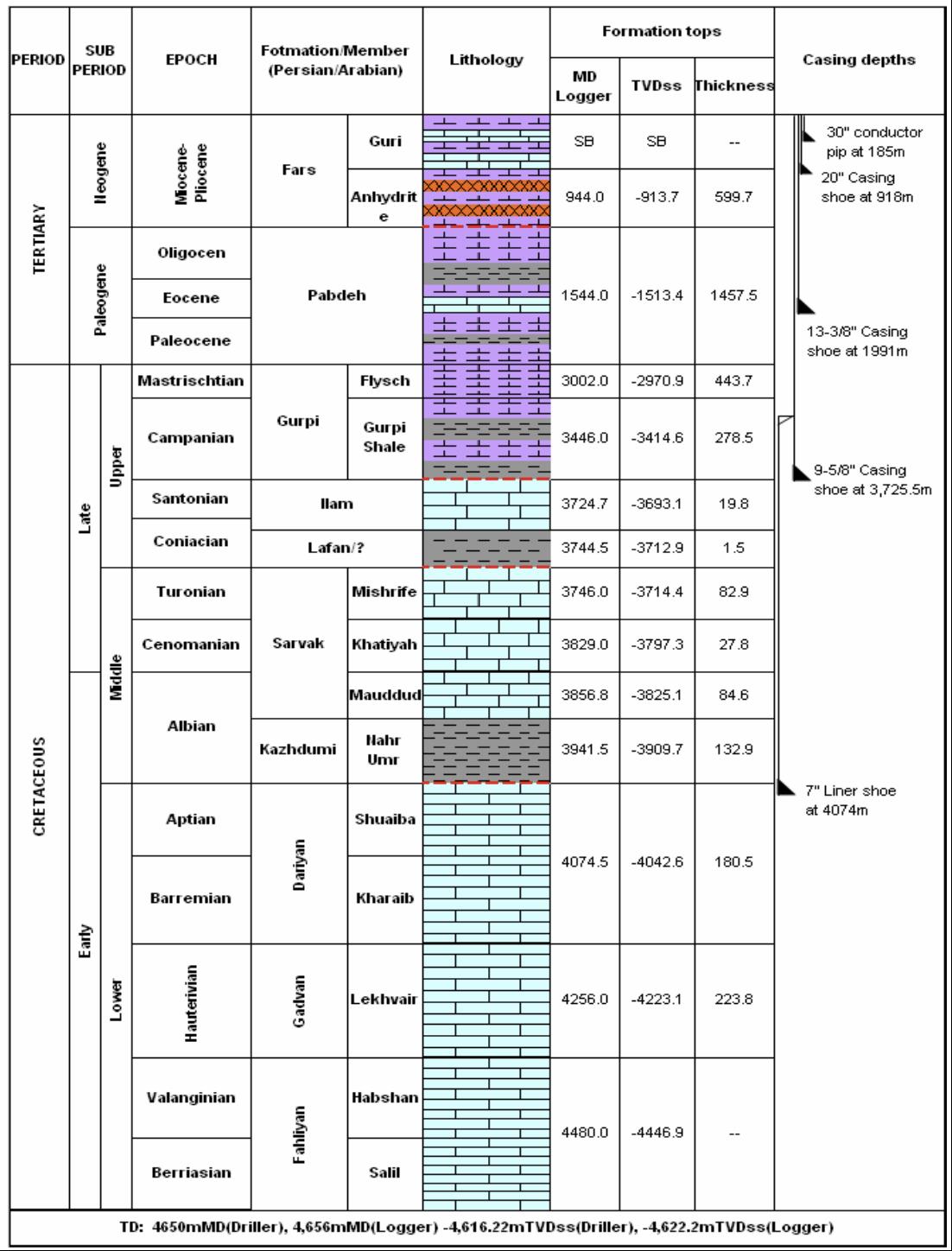
Hengam oil-field in the Persian Gulf is located 40 km south of Qeshm Island and 30 km south of Hengam Island in the Strait of Hormuz. Hengam oil-field is a joint field between Iran and Oman with a water depth of 70 m. This field is located on the top of Ilam Formation and its direction is north to south, which corresponds to the main direction of Oman Mountain. Hengam oil-field was discovered in 1975 by drilling well number 1. This well was tested in Ilam and Sarvak constructions and production started from this well after perforation. Well A of Hengam oil-field has been drilled 1400 m north of well number 1 of this field and its main reserveoirs include Ilam, Sarvak, Darian and Fahlian formations. Hengam oil-field belongs to the active salt dome of Hormuz geograpgically like many fields in the Persian Gulf basin, which dates back to the Precambrian era.
Well A from Hengam oil-field is an appraisal well that has been drilled to obtain more geological and reservoir information in this field before the start of Hengam oil-field development. Preliminary studies also show that Bangestan group (Ilam and Saruk formations) are the main hydrocarbon reservoirs .

Fig. 1. Geological structure of well An in Hengam oil-field
The main formations of Ilam and Sarvak often consist of limestone lithologically with a small inner layer of shale. Illite is considered as the main clay in these formations. Limestone is dense in these formations and has poor initial porosity. Gurpi Formation has two parts in Hengam oilfield, which Gurpi-Shale section in Hengam oil-field plays the role of caprock for Ilam and Sarvak formations.
The main composition of Ilam Formation with a thickness of approximately 20 m based on petrophysical data is limestone and the percentage of porosity in this formation is between 0 to 15 and also has an average net porosity of 9.78%, a water saturation percentage of 8.26% and an average permeability of 13.16 mD. Sarvak Formation consists of three parts: Upper Sarvak, Middle Sarvak and Lower Sarvak, which mainly contain limestone. The geological structure of well A of Hengam field is shown in Figure 1. Data related to these graphs are available from a depth of 2729 to 3912 m.
Data source: Construction of Mechanical Earth Model (MEM) to determine the goemechanical properties of reservouirs: a case study. Annabelle Graham, Emma Scott, William Ward
Следующее Месторождение: Juraybiat 2